stroke victim life expectancy
 Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should Know
Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should KnowPrognosis and life expectancy Every year, nearly 800,000 people in the United States have a brain attack, either their first time or a repetition. Although some blows are devastating from the beginning, the damage of a stroke can be limited with rapid treatment. It is difficult to say immediately how much a stroke will affect your life, temporarily or permanently, as your perspective depends on the type of stroke you had, where the blockage or bleeding occurred in the brain, and how much damage it caused. Learn about the different types of strokes, survival rates, rehabilitation of strokes and life after stroke. Treatment Type Defines treatmentIn addition to transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), or mini strokes that solve on their own, the two main types of stroke are ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes occur when something blocks blood flow to a part of your brain. This is the most common type of stroke, which affects 87% of people in the United States who have a stroke. Treatment involves trying to dissolve deposits or fatty deposits, or manually remove them, to allow normal blood flow to return to the brain. If this is done fast enough and effective, there may be limited or unsustainable damage to the brain tissue. A hemorrhagic attack is weirder. It occurs when the blood flows from a broken or leaky blood vessel and because the skull is a closed compartment, excess blood creates pressure on the surrounding brain tissue. If you take an anticoagulant (blood thinner), the first step is to stop that medication to encourage your blood to coagulate and stop flowing into the neighboring brain tissue. Other treatment options include surgery to stop bleeding. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation How well you recover from a stroke depends on many things, apart from the severity and location of the stroke itself. They include: Some people recover completely from a stroke; some are left with lasting problems; while others are completely disabled. Most progress in recovering strokes is made during the first 6 to 12 months after the event. Of course, you can still see improvements over time, but most progress is in the first year. Within the first months after stroke, certain parts of the damaged brain tissue can be cured. Any progress after the first year is mainly due to rereading the way to do things or to compensate, rather than healing the brain itself. There are many long-lasting effects that could remain after stroke, such as:Treatment to Improve Prognosis and Life ExpectationThe treatment within an hour of stroke gives patients the best chances of a good recovery. Time is of the essence, so act "FAST" when you see the symptoms of a stroke: Facial drawing, Arm, Difficulty of speech means it's time to call 911. FASTDepending on the type of stroke, doctors can choose from a variety of treatment options for strokes, including: Your doctor may recommend additional treatments based on your individual stroke and medical history. Recovering from a Stroke Once the immediate danger has passed, the process begins to recover from the effects of stroke. Some people recover completely, but if you have some persistent problem, the more work is done at this early stage, the better the chances of a more complete recovery. The type of rehabilitation you need will depend on the side of the brain that holds the stroke. The strokes on the right side of the brain can leave you with difficulty moving the left side of your body. It can also have difficulty talking and swallowing. The damage to the left side of the brain can leave you with difficulty moving the right side of the body. If you are sent to a rehabilitation center, you can see a , , and/or a speech therapist, which can evaluate the ability to swallow as well as speech. You can also see or address any psychological problems you may experience after a stroke. If you are sent home instead of a rehabilitation facility, your doctor will likely give you exercises to do on your own or schedule appointments for you to see physical therapists to help ensure that you are making progress in your recovery. Recovery Assessment There are several scales of evaluation of strokes. The most common ones used during the acute phase, right after the stroke, are the Glasgow Coma Scale, the Stroke NIH Scale, the NIHSS Modified Scale and the Intracerebral Hemorragia Scale. These scales take into account how you are responding to commands, reviewing your eye responses, verbal responses and motor responses (movement). They also look for how they understand questions and directions. Once the dangers of the stroke have passed, it can be evaluated for functional capacity - what works well since the stroke. The Modified Rankin Scale, one of such assessments, looks at your ability to walk independently, if you can live alone, and if you can return to your activities from before the stroke. Other scales evaluate your mental state, alert, if you can perform personal care, and more. These assessments help the stroke team to determine the best recovery and rehabilitation plan for each individual. Evaluations also give an idea of what life expectancy can be. The worse the lasting effects are, the greater the risk of dying before someone who has not had a stroke. Life after a stroke Once you have had a stroke, you will be followed closely by your doctor, even if you do not have lasting effects. If the stroke was caused by a condition, such as or endocarditis, then it will have to be treated for those conditions to reduce the risk of a second stroke. If the stroke was caused by a blood clot, you may have to take an anticoagulant to prevent additional clots. It's important that you follow the advice of your trazo team. Assist all medical appointments and take the recipes as they are given. Report any changes to your health to your brain spill doctor and make sure any other health care provider (including dentists) knows you have a history before any treatment. Even your pharmacist should know how to protect against any interaction or medication that may put you at risk for another stroke, in particular medications or over-the-counter supplements. After recovering from a blow, it is natural to fear having another. By following your treatment plan, you reduce that risk. Up to 75% of the survivors of the stroke never have another. But that means that 25% of people who have a stroke will have another one within five years. Be prepared to ensure that those around you can recognize the symptoms of a stroke and know how to call 911 immediately. By working with your shock treatment team, your personal support network, family members and caregivers, you can improve your chance of successful beating recovery and reduce your risk of future blows. About the author Silence Silence Silence © Copyright 2020 Healthgrades Operating Company, Inc. Patent US Nos. 7,752,060 and 8,719,052. All rights reserved. Third party materials included here protected under copyright law. The use of this website and any information contained here is governed by the . Healthgrades content does not provide medical advice. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
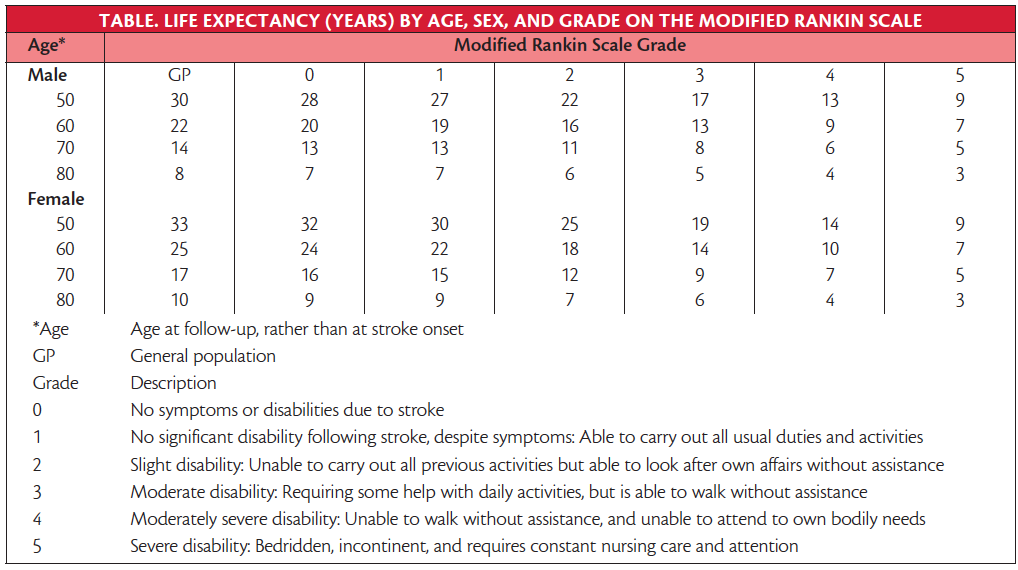
Long-Term Survival Prognosis After Stroke - Practical Neurology

Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should Know
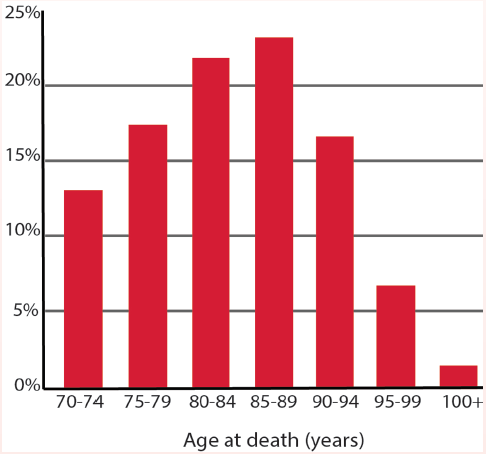
Long-Term Survival Prognosis After Stroke - Practical Neurology
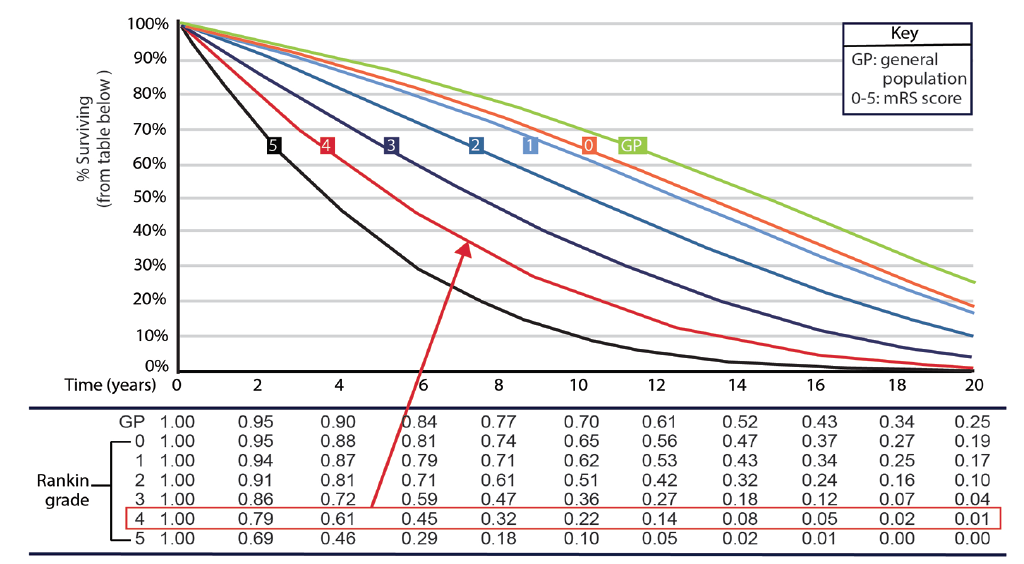
Long-Term Survival Prognosis After Stroke - Practical Neurology

Life Expectancy After A Brain Stroke? - Medicover Hospitals

Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should Know

Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should Know
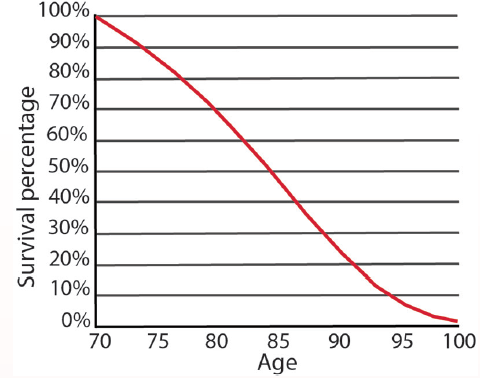
Long-Term Survival Prognosis After Stroke - Practical Neurology

Life Expectancy after Stroke Based On Age, Sex, and Rankin Grade of Disability: A Synthesis - Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases

Long-Term Survival and Causes of Death After Stroke | Stroke
Life Expectancies Among Survivors of Acute Cerebrovascular Disease

Massive Stroke: Recovery Timeline & Prognosis - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com

Stroke Outcome in Those Over 80 | Stroke

ePainAssist | Brain stem, Patient experience, Spinal cord injury

Life Expectancy for CP, VS, TBI and SCI

Long-Term Survival and Causes of Death After Stroke | Stroke
Massive Stroke: Symptoms, Treatments, and Long-Term Outlook

Age‐specific clinical characteristics and outcome in patients over 60 years old with large hemispheric infarction - Li - 2018 - Brain and Behavior - Wiley Online Library

Life Expectancies Among Survivors of Acute Cerebrovascular Disease | Stroke

Hemorrhagic Stroke: Survival Rate, Life Expectancy & Recovery - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
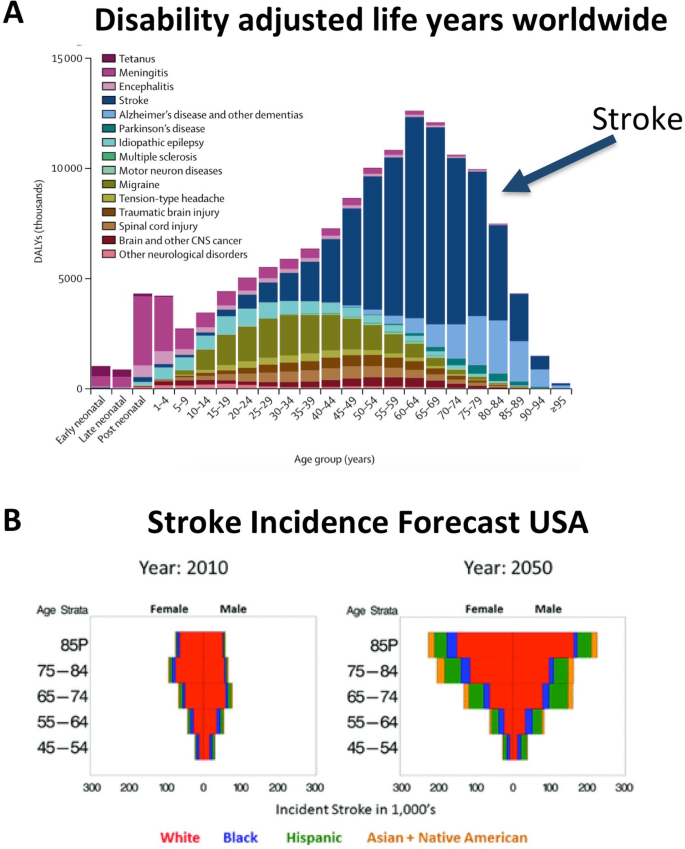
Recovery from stroke: current concepts and future perspectives | Neurological Research and Practice | Full Text
![PDF] Quality-Adjusted Life Expectancy (QALE) and Loss of QALE for Patients With Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A 13-Year Follow-Up | Semantic Scholar PDF] Quality-Adjusted Life Expectancy (QALE) and Loss of QALE for Patients With Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A 13-Year Follow-Up | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1a66b32eefbe6e7139cb9b38ba3bbb5fb7edb751/2-Table1-1.png)
PDF] Quality-Adjusted Life Expectancy (QALE) and Loss of QALE for Patients With Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A 13-Year Follow-Up | Semantic Scholar

Burden of CKD and Cardiovascular Disease on Life Expectancy and Health Service Utilization: a Cohort Study of Hong Kong Chinese Hypertensive Patients | American Society of Nephrology
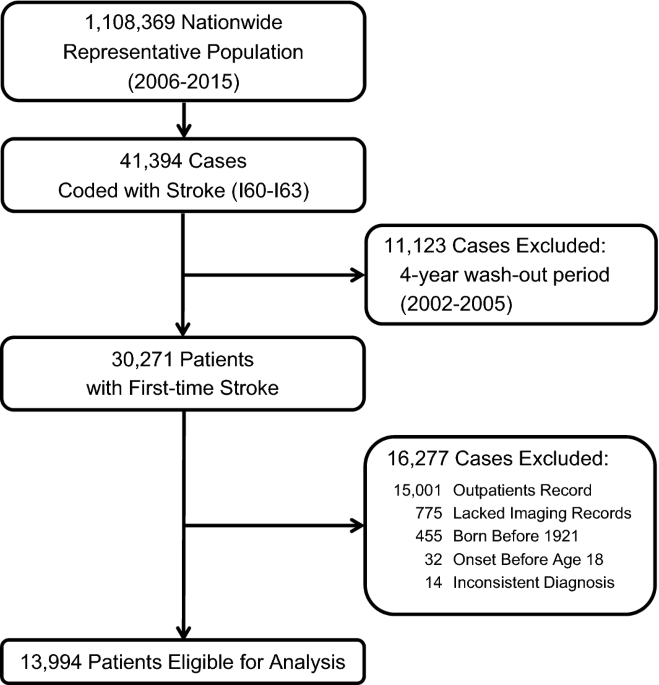
Lifetime risks and health impacts of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke in South Korea | Scientific Reports
Stroke in Elderly Adults: Signs, Symptoms, Prognosis | Griswold
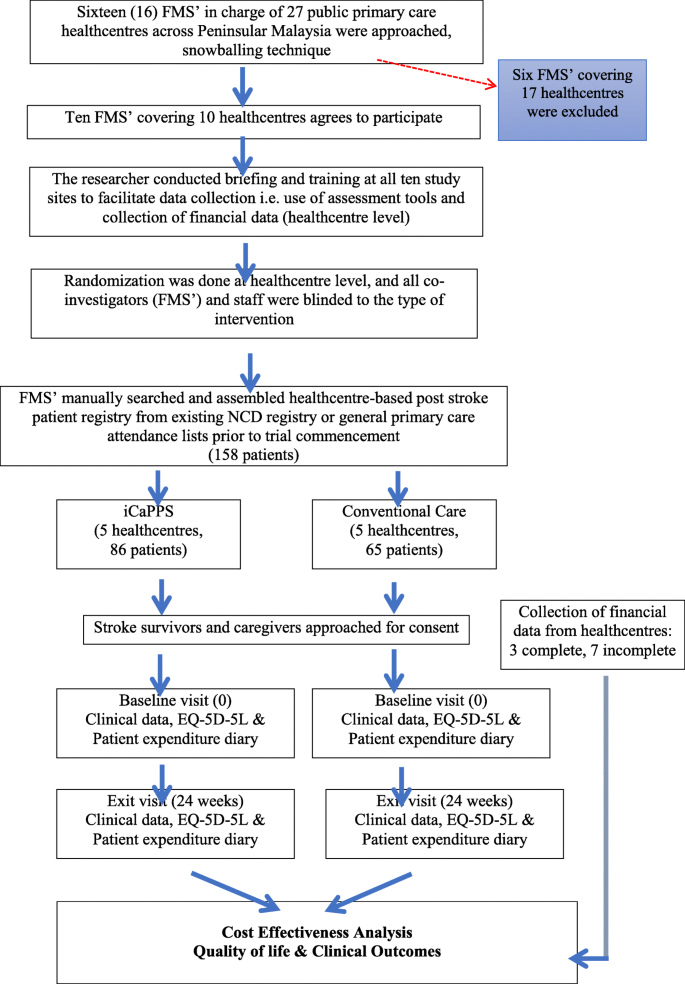
The integrated care pathway for managing post stroke patients (iCaPPS © ) in public primary care Healthcentres in Malaysia: impact on quality adjusted life years (QALYs) and cost effectiveness analysis | BMC

14 Warning Signs and Symptoms of Stroke FAST (Mini, TIA)

Stroke Prognosis & Life Expectancy | Stroke Recovery

Weighting Components of Composite End Points in Clinical Trials | Stroke

Predictors of Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A 1-year Follow-Up Study of a Tunisian Sample - ScienceDirect
Estimation of expected years of life lost for patients with ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage | Emerald Insight

Factors associated with physical and psychosocial problems among Indian stroke survivors Sharma M, Lal M, Singh T, Deepti SS Indian J Palliat Care

Determinants of the decline in mortality from acute stroke in England: linked national database study of 795 869 adults | The BMJ

Stroke Statistics: Stroke Survival Rate and 8 Other Facts You Should Know

Decision Making in Acute Stroke Care | Stroke

Blogging Stroke – The Acute Ischemic Stroke Patient with Cerebral Microbleeds — When is IV Thrombolysis Beneficial?
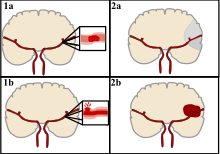
Stroke - Wikipedia
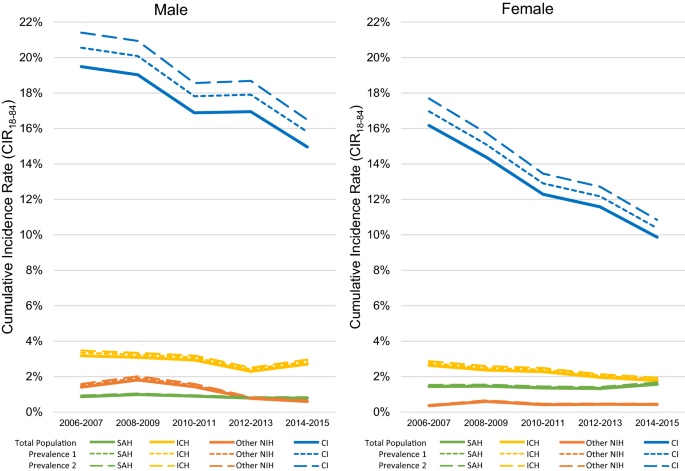
Lifetime risks and health impacts of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke in South Korea | Scientific Reports

Establishing Goals of Care for Patients With Stroke and Feeding Problems: An Interdisciplinary Trigger-Based Continuous Quality Improvement Project - Journal of Pain and Symptom Management
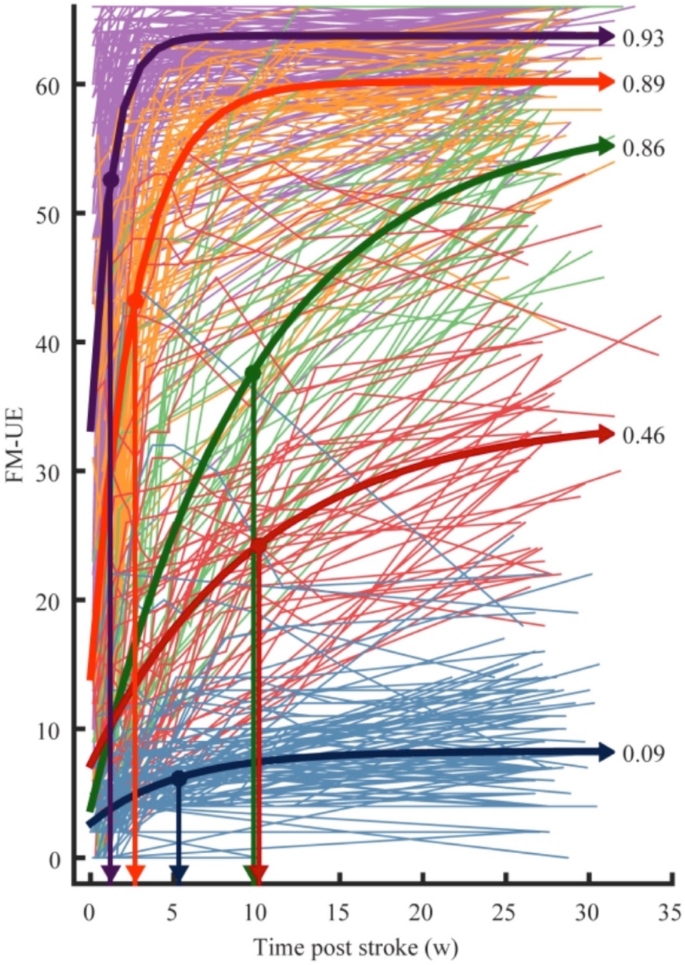
Recovery from stroke: current concepts and future perspectives | Neurological Research and Practice | Full Text
Posting Komentar untuk "stroke victim life expectancy"